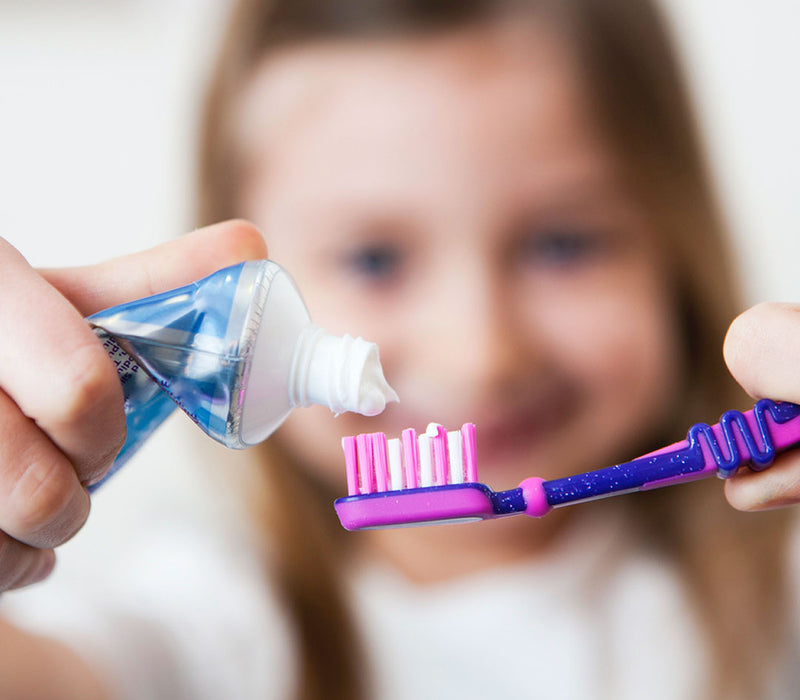
Fluoride, which is often present in toothpaste, offers numerous benefits for dental health. It helps strengthen tooth enamel and prevent cavities. But why should one spit out toothpaste with fluoride after brushing?
Here are some reasons:
Excess Fluoride: Excessive fluoride intake, especially at a young age, can lead to fluorosis. Dental fluorosis can result in white or brown spots on the teeth. This is typically only a cosmetic issue, but it indicates that too much fluoride has been consumed.
Low Amounts Needed: Only a small amount of fluoride is required for its cavity-preventing effect. Therefore, it is not necessary to swallow toothpaste to benefit from the advantages of fluoride.
Risk of Poisoning: Even though the amounts of fluoride in toothpaste are generally safe when used as directed, swallowing large quantities of fluoride-containing toothpaste (e.g., an entire tube) can lead to symptoms of fluoride poisoning. These symptoms may include stomach discomfort, nausea, and, in very rare cases, more serious health issues.
Hence, it is advisable to spit out toothpaste after brushing and not swallow it. It's especially important to ensure that children use a pea-sized amount of toothpaste and understand that they should not swallow it.
What is fluoride and what is it good for?
Fluoride is a naturally occurring chemical element that has many applications, especially in dental care. Here is some information about what fluoride is and what it is good for:
1. Dental Health: Fluoride is known for its crucial role in promoting dental health. It strengthens tooth enamel and helps prevent tooth decay by making teeth more resistant to acid attacks. Fluoride can remineralize early-stage existing cavities.
2. Cavity Prevention: Fluoride is a key component of toothpaste, mouthwashes, and professional teeth whitening products. It is commonly used in cavity prevention and treatment.
3. Drinking Water: In some countries, fluoride is added to drinking water to promote the overall dental health of the population.
4. Dental Treatments: Fluoride can also be applied in the form of fluoride varnishes or gels in dental practices to directly strengthen and protect teeth.
5. Pediatric Dental Care: Fluoridated toothpaste is important for children to protect their teeth from an early age and prevent cavities.
6. Nutrition: A balanced diet can also contain fluoride, especially in foods such as fish, tea, and some drinking water.
It is important to note that the proper dosage of fluoride is crucial to reap its benefits without risking negative effects like fluorosis or overdose. Generally, the use of fluoride toothpaste in children should be done under adult supervision, and dentists can provide individual recommendations for fluoride intake.